“Cybersecurity is a social responsibility. We all have a role to play.” ~ Magda Chelly.
Before we dive in more depth into SSL certificates and their functions, we need to understand why we need to secure our user’s connection to our server.
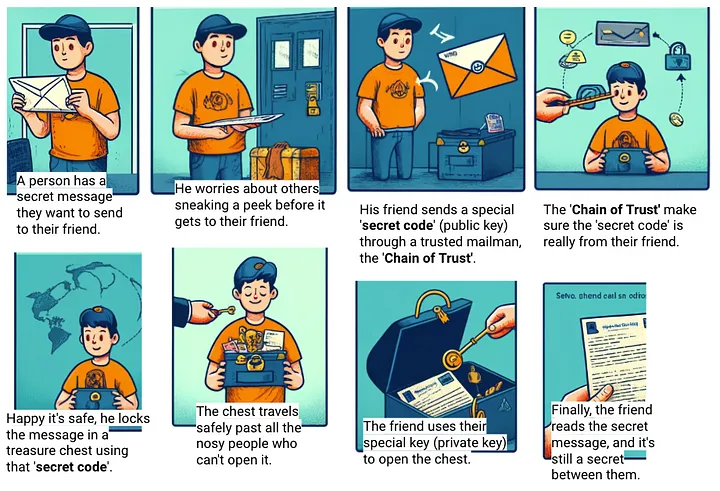
Imagine sending a postcard through the mail. Anyone who handles it along its journey can read your message. Now, imagine instead that you could send a sealed letter and its content visible only to you and the recipients. This is the essence of what SSL/TLS certificates do for our online communications.
The reasons for securing our website connections include:
- We must protect user data to ensure our website is legit and trustworthy.
- When we encrypt users’ data, we comply with data protection regulations and industry standards.
- Enhance user experience as well as enhance the brand image from the feeling of safety that your users have whilst accessing the information on your site.
What Are SSL/TLS Certificates?
Now, let’s dive into what an SSL certificate is and how it works.
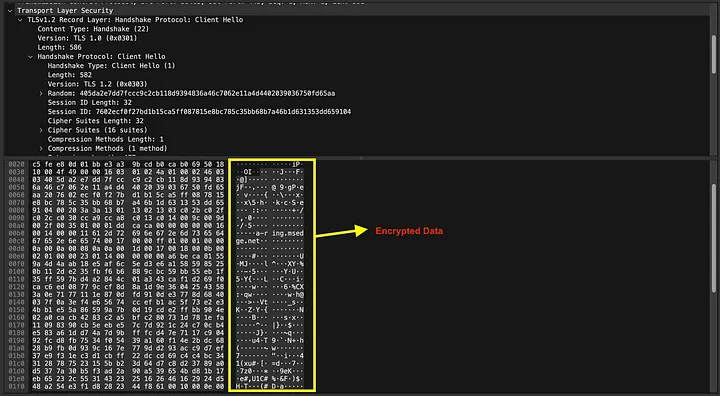
- Definition: SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and its successor, TLS (Transport Layer Security), are protocols for encrypting internet traffic and verifying server identity. Every SSL/TLS certificate serves as a digital passport for a website, ensuring that the data exchanged between a user and the site is inaccessible to outsiders. Think of it as having a secret code for conversations between your website and your users; only they can understand each other.
- Real-Life Applications of SSL/TLS Certificates:
- E-commerce Platforms: SSL/TLS certificates are important for securing online transactions and protecting customers’ sensitive information on said platforms while shopping online. E-commerce platforms deploy SSL/TLS certificates to encrypt customer’s payment details and ensure the confidentiality of financial transactions.
- Banking Websites/Apps: Financial institutions rely on SSL/TLS certificates to safeguard clients’ financial data. By encrypting login credentials, account information, and transactional data, SSL/TLS certificates mitigate the risk of unauthorized access and fraudulent activities. This will bolster customer’s trust as well as improving users experience while using their site/apps.
- Healthcare Portals: Healthcare organizations leverage SSL/TLS certificates to secure patients’ sensitive medical information from unauthorized access or interception. Therefore, complying with stringent regulatory requirements such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
3. The crucial role of SSL/TLS:
- Data Security: By protecting sensitive users’ information from interception by hackers or eavesdroppers, your site will gain more trust and credibility from your users.
- SEO Benefits: Google search engines prioritize secured websites in their search results, thus giving SSL-secured sites a ranking boost. It is essential for improving visibility and driving organic traffic.
- Regulatory Compliance: Data protection regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) mandate the use of SSL certificates to protect users’ data.
What Are the Types of SSL Certificates?
There are lots of SSL certificates in various types that cater to different needs. While one certificate could secure a single website, another could secure multiple websites. Below are the types of SSL certificates depending on how many domains could be linked to a certificate:
Single-Domain SSL Certificate:
As the name suggests, a single-domain SSL certificate is specific to one domain and can’t be used to secure any of its subdomains. For example, if www.example.com as a root domain is secured by these certificates, then www.example.blog.com is not secured by the same certificate. The easiest way to check it is to see the Common name and the SANs on the certificate. For a Single-Domain SSL certificate, both values should exactly match and only contain a single domain name.
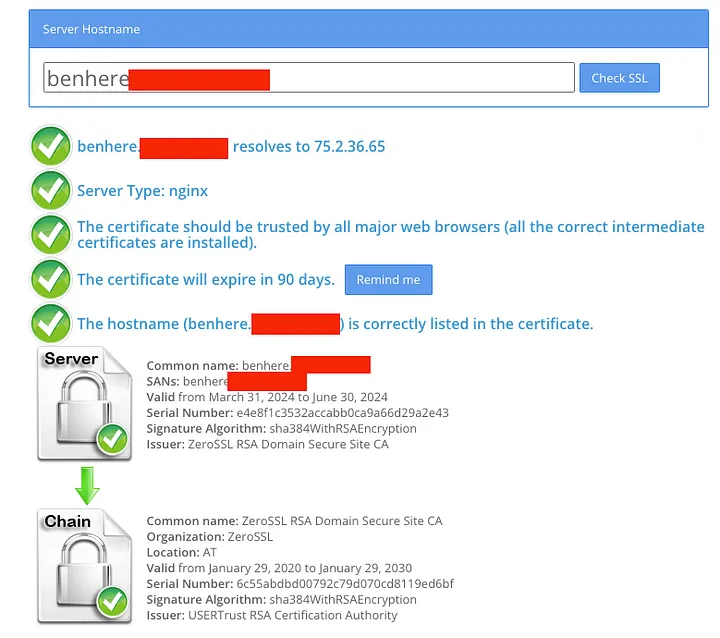
Multi-Domain SSL Certificate:
Different from a single-domain SSL certificate, a multi-domain certificate is designed to secure multiple domains (related or not) under one certificate. This is useful if you’re managing a group of different websites and allows you to manage all their security under one SSL certificate.
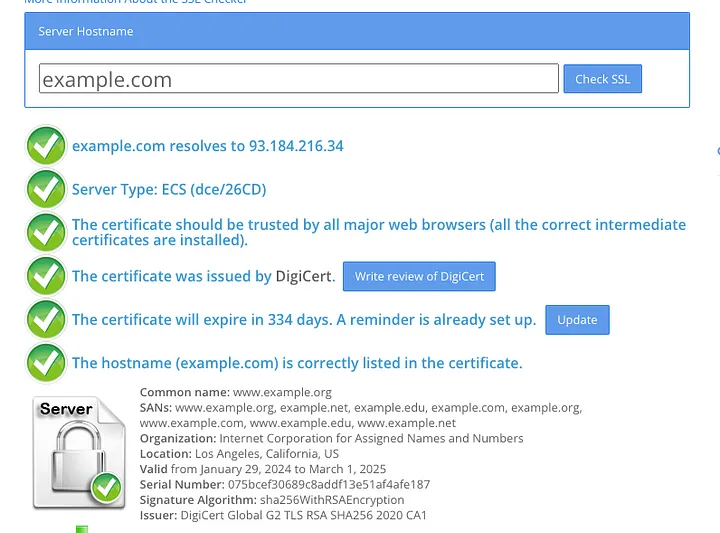
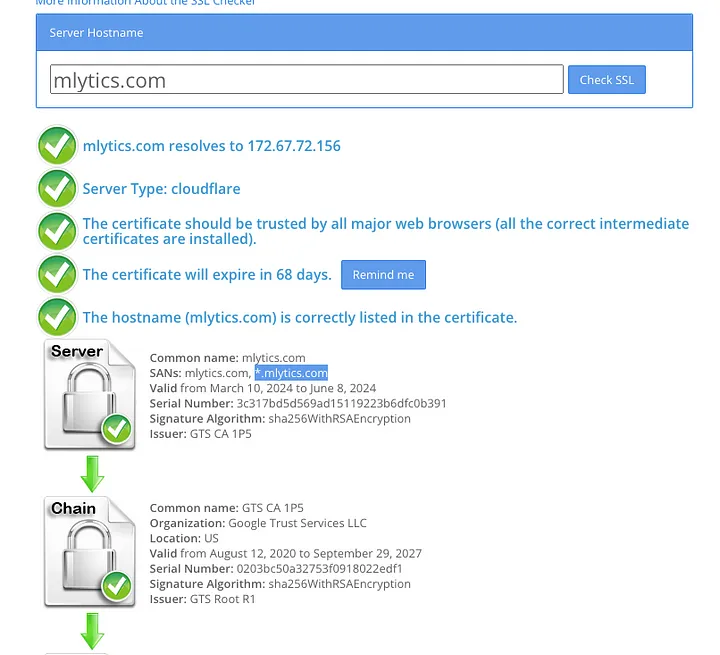
Wildcard SSL Certificate:
Wildcard SSL certificate is an in-between of Single and Multi-domain certificate, as it covers the main domain and all of its subdomains. So if for example, you have a wildcard certificate for *.example.com, it will secure blog.example.com and test.example.com as well.
To summarize, SSL/TLS certificates facilitate secure communication between a server and a user, protect sensitive data, and instill trust among users. This is especially important in the digital age.
Although we’ve tried everything we could to secure our sites/apps, please keep in mind that there’s always a place and time to ask for experts’ help and save our resources (capital and time) in securing users’ data. This means that, even if we know how to secure our business (sites and apps), in some cases, it might be better to focus on the services that we offer to users instead.
Thank you for reading this article, and don’t forget to clap and leave a comment down below, as it will help us grow and motivate us to deliver more quality content in the future.